Our lead asset, BRM421, is on track to become a first-in-class treatment for Dry Eye Disease (DED) which treats and repairs corneal damage.
BRIM Biotechnology is accelerating the cycle of innovation by leveraging its PDSP platform to bring novel ophthalmology treatments to market.
About Dry Eye Disease
Dry eye disease (DED) is a common ailment in industrialized and aging societies, with complex, multifactorial etiology. The prevalence of this ocular disease varies depending on geographical weather, season, and lifestyle. The global prevalence ranges from 5% to 50%, with females generally having 1.3 to 1.5 times higher prevalence than males. The prevalence among Asian populations is also relatively high and increases rapidly with age.
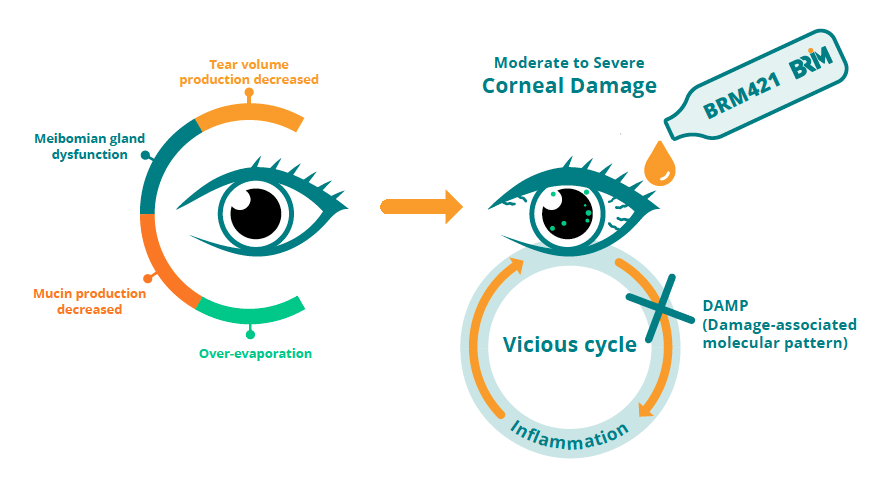
DED patients are mainly divided into two types: those with insufficient tear secretion and those with excessive evaporation due to the changes in tear film composition, leading to unstable tear film to properly maintain the ocular surface moisture. Both result in ocular dryness, ultimately causing damage and shedding of conjunctival and corneal epithelial cells. This leads to symptoms such as redness, hyperemia, itching, sensitivity to wind and light, blurry vision, stinging, foreign body sensation, viscous discharge, and reflex tear secretion. In severe cases, filamentous adhesions may form due to corneal epithelial breakdown, leading to corneal-conjunctival lesions, visual impairment, and other significant complications, thereby affecting vision, workability, and quality of life.
The tear film is mainly composed of lipids secreted by the meibomian glands, mucin secreted by goblet cells, and water. When tear secretion is insufficient, meibomian gland dysfunction occurs, mucin production decreases, and tear evaporation increases, resulting in damage to ocular surface epithelial cells. This further leads to an inflammatory response mediated by damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), causing secondary damage to ocular surface epithelial cells in a vicious cycle.
Proposed MoAs of PDSP for DED treatment
Animal experiments have confirmed that PDSP can promote LSC proliferation and effectively repair mouse corneal damage caused by dryness. In addition, based on its known mechanisms of action, PDSP has the potential to improve tear quality by repairing meibomian glands and goblet cells. It can restore corneal nerve function via its neurotrophic property to improve vision. It also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, which may inhibit inflammation induced by DAMPs to disrupt the vicious cycle of corneal damage in DED.
Compared to existing competitors, it is the only drug capable of treating DED through multiple mechanisms. Upon confirmation in phase III clinical trials, it will offer DED patients a comprehensive treatment option.
Accelerate corneal repair
Activate limbal stem cells
Improve tear quality
Maintain goblet cell number
Restore meibomian glands
Improve visual functions
Promote neurotrophic tissue protection
Break vicious cycle
Inhibit inflammation
BRM421:first-in-class drug for DED
INDICATION
Dry Eye Disease (DED)
MECHANISM
First-in-class, novel neurotrophic peptide that can activate stem cells, improve tear quality and visual function, and break the vicious cycle
ADVANTAGES
- Activate stem cells for tissue repair
- Improve tear quality and visual function
- Early onset
- Strong safety profile
MARKET
- Growing patient population particularly in younger age group
- Global market of USD ~ 7.02 billion in 2023, and projected to be USD ~13 billion in 2032
COMPETITION
Xiidra (Novartis) and Restasis (Allergan) own the majority of the US market share with multiple competitors in late clinical stage
DEVELOPMENT STAGE
Next Phase 3 is scheduled to be initiated by 2025

The key niche value of BRM421

BRM421 treats DED by multiple MOAs to ensure efficacy and give patients better treatment options

BRM421 improves signs and symptoms in 2wks showing early onset compared to anti-inflammation drugs

With over 80% profit margin, BRM421 can be priced affordably at half of the current drug price

BRM421 has no drug-related SAE. No patient dropout due to treatment in 3 clinical trials, with over 1000 patients
BRM421 development timeline